So far, we've discussed the myths propagated about abnormal breastfeeding, how to examine for tongue-tie and the various symptoms that arise from breastfeeding a tongue-tied baby for both mom and baby. This post will explain the mechanism by which the tongue-tie affects breastfeeding.
Before defining how breastfeeding actually occurs, it's important to clear up some misconceptions. How does a baby actually breastfeed? Here are some older theories for the mechanics of breastfeeding:
- The baby sucks on the nipple as if it were the end of a bottle
- The baby uses the lips and tongue to strip the breast (e.g. milking the breast)
- The baby just drinks breast milk (believe me, I've heard this)
The most common misconception is the second of those mentioned. People think that the breast fills up with milk, and it is the baby's job to remove that milk by undulations of the tongue and upper lip in a milking movement. Ultrasound data show us that this isn't true. Occasionally, the first and third misconceptions do happen. When a baby is tongue- or lip-tied, they will cheat down to the end of the nipple and will nipple feed instead of breastfeed. And in some instances, when mom has an overactive letdown or oversupply, the baby has to exert very little effort and just drinks what is presented. This isn't a sustainable method of nursing.
The best data to date come from ultrasound studies. These studies show two important concepts:
- They show the minimal involvement of the nipple in children without tongue-tie and conversely, a mechanism for the damage that occurs to the nipple in the tongue-tied child
- They show that the mechanism of nursing depends on the baby generating negative pressure inside the mouth, which draws the milk out
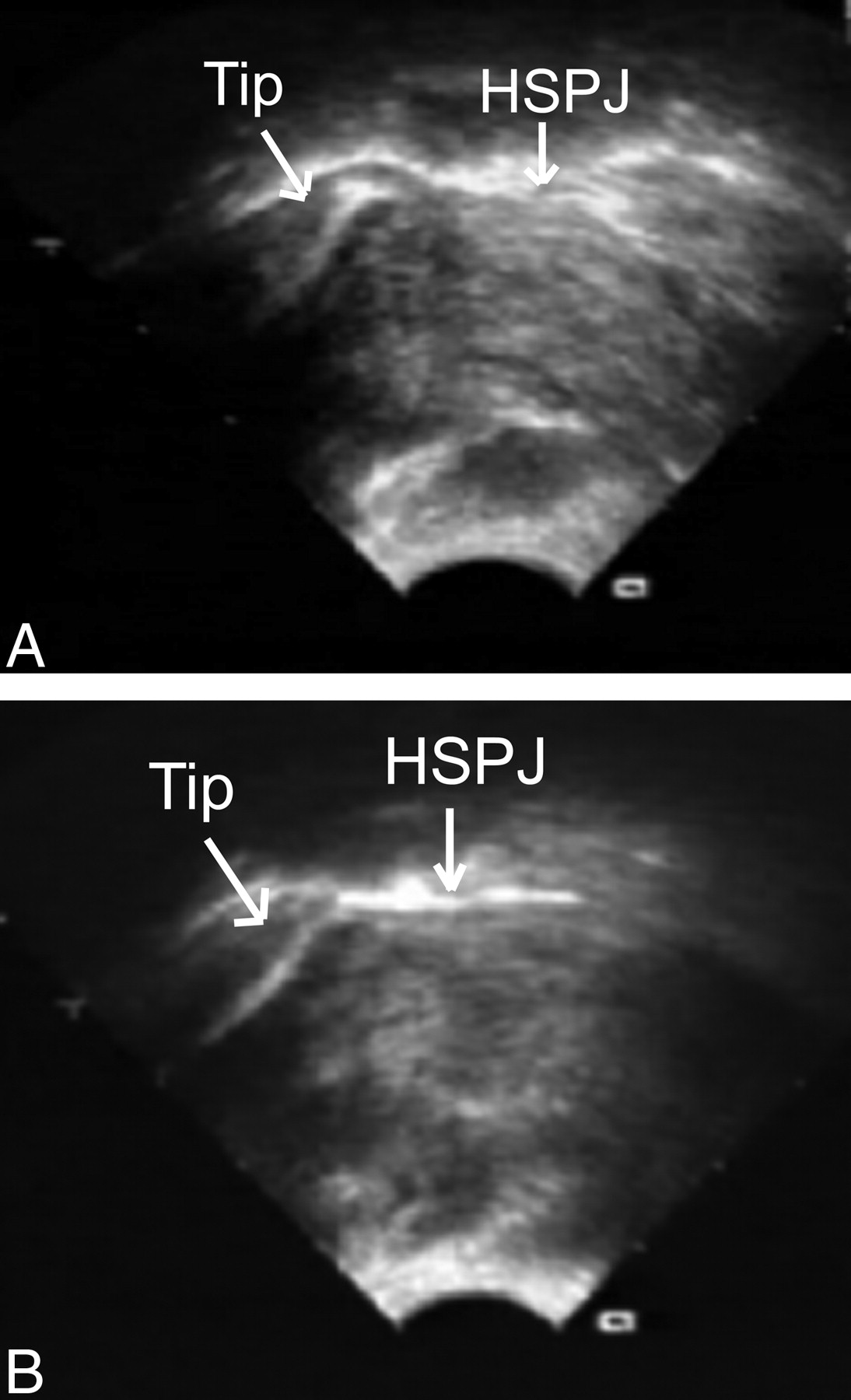
Panel A shows a tongue-tied baby compressing the nipple tip. Panel B shows less compression following a frenotomy. From Geddes 2008. (HSPJ = hard/soft palate junction)
What happens to the nipple while inside the baby's mouth?
The data from Geddes' study show two separate patterns of nipple positioning when a baby is tongue-tied. Interestingly, I have seen this in the babies in my office who cause two different patterns of nipple damage. The first pattern occurs when the nipple is in the appropriate position in the mouth, which is at the junction of the hard and soft palate (further back than most people think). These tongue-tied babies are able to get around the length of the nipple but tend to clamp down and bite at the base of the nipple. Clinically, this can result in creasing and blanching at the base of the nipple. The second pattern occurs when a baby uses the tongue to block or thrust the nipple forward in the mouth. These babies are unable to keep the nipple in the appropriate position, so the damage is more on the nipple itself rather than around it. This may also explain why some babies are unable to tolerate a bottle or a pacifier. Instead of moving freely, the tether of the tongue forces the tongue to move in a forward, rather than an upward, motion. Why a tongue-tied baby uses one tongue motion over the other is unknown.
What are the mechanics of breastfeeding?
Now that we understand that the baby does not physically "milk" the breast, let's look at what a baby does to draw milk out of the breast. Again, we will turn to the ultrasound studies. The most plausible explanation for how a baby nurses involves the generation of negative pressure (a vacuum of sorts) within the oral cavity using an up and down motion of the tongue. First, the baby must have the ability to form a seal around the breast. This involves the upper lip flanging outward and the tongue cupping and elevating the breast towards the palate. If the tongue cannot elevate, cupping can be quite weak and the baby can "fall" off the breast. As important is the ability for the midportion of the tongue to freely elevate and depress within the oral cavity. This is how the baby draws milk out of the breast - the baby will push their tongue up towards the palate and then quickly depress it, creating a vacuum.
Please spend a moment to watch this brief video of an ultrasound showing the motion of the tongue in generating this negative pressure. Pay special attention to the fact that the nipple itself is not manipulated much in a baby that isn't tongue-tied.
These data demonstrate that breastfeeding is less about the nipple and more about the depth of the latch and the mobility of the tongue. It explains how many babies with no visible tongue-tie can still have terrible latches. These posterior tongue ties are more hidden, but still cause significant restriction of movement (in that critical upward direction). It also explains why a baby's ability to stick the tongue forward is irrelevant in assessing whether tongue-tie exists.
The Geddes studies show us the importance of thinking about a baby's anatomy and how it will impact breastfeeding. I will make a similar argument when we discuss the importance of a tethered upper lip. If anatomy is preventing the latch from being initiated, a domino effect of compensatory movements begins. Prevention of that compensatory domino effect is critical in maintaining a long-term nursing relationship.
Reference: Geddes, et al. Frenulotomy for Breastfeeding Infants With Ankyloglossia: Effect on Milk Removal and Sucking Mechanism as Imaged by Ultrasound. Pediatrics. 122:1; e188-e194.